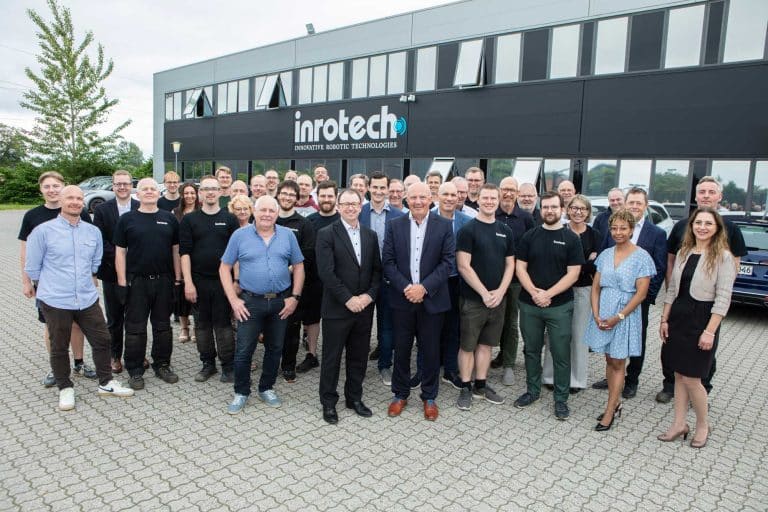
Lincoln Electric ® acquires Inrotech A/S
Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,

Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,
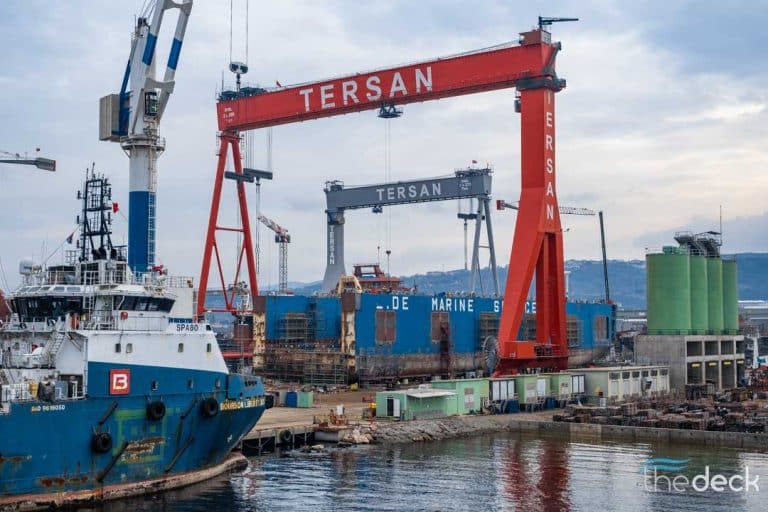

Inrotech has received an order from Tersan Shipyard, a diversified company with expertise in constructing LNG and battery-operated vessels, as well as various value-added niche

Inrotech welcomes Henrik Lenskjold as its new Chief Executive Officer. Henrik, who served as the Chief Operation Officer at Inrotech for six years, has been
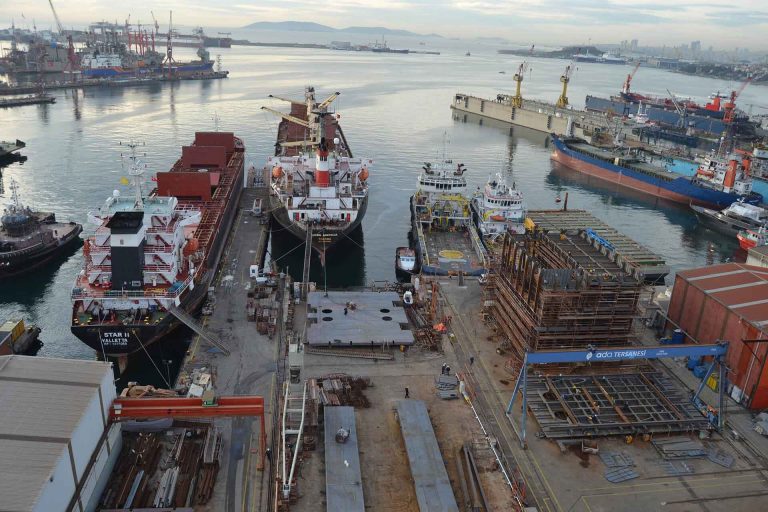

Welding robots originating from Denmark have gained substantial popularity within the Turkish shipbuilding industry for the welding of ship panels. Ada Shipyard, a prominent shipyard
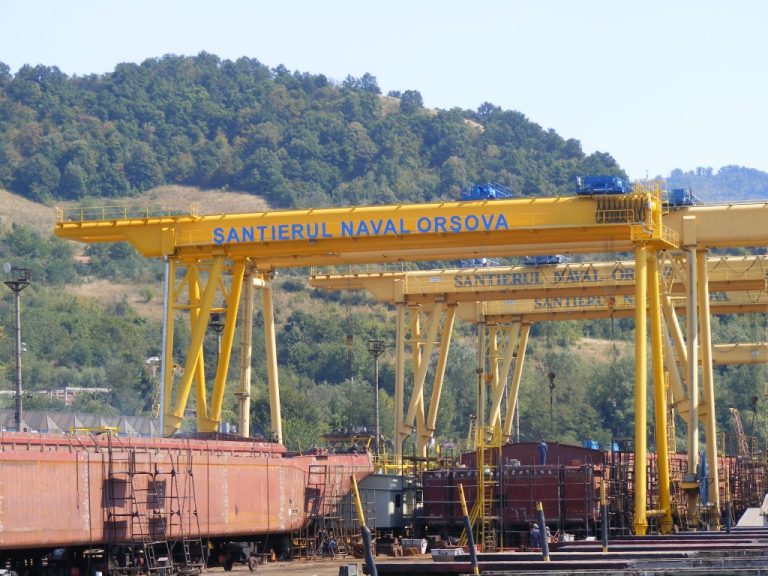

Inrotech has received an order from Santierul Naval Orsova Shipyard, a leading shipbuilder in Romania. The company invest in high quality welding automation as a

The growing need for skilled welders in offshore wind and shipyards worldwide has placed a huge demand for labor in these sectors. Numerous manufacturers experience
As the industry leans towards innovation, 2026 is set to be pivotal for robotic welding automation. Experts predict significant transformations in how businesses will integrate robotics into their workflows. Dave Robinson, a leading figure in automation, emphasizes, “The future of manufacturing relies on the precision and efficiency of robotic welding automation.”
In recent years, robotic welding automation has made substantial strides. Companies are now improving product quality and reducing labor costs. However, the transition is not without challenges. Many organizations struggle with adapting their existing infrastructure. The notion that robots can replace human oversight completely is flawed. Human judgment remains vital in maintaining quality control.
Looking ahead, maintaining flexibility is crucial. The industry must navigate both technological advancements and workforce changes. Companies should prepare for potential disruptions while embracing the idea that robotic welding automation is a tool, not a total solution. The journey ahead holds promise and uncertainty, requiring ongoing reflection and adaptation.
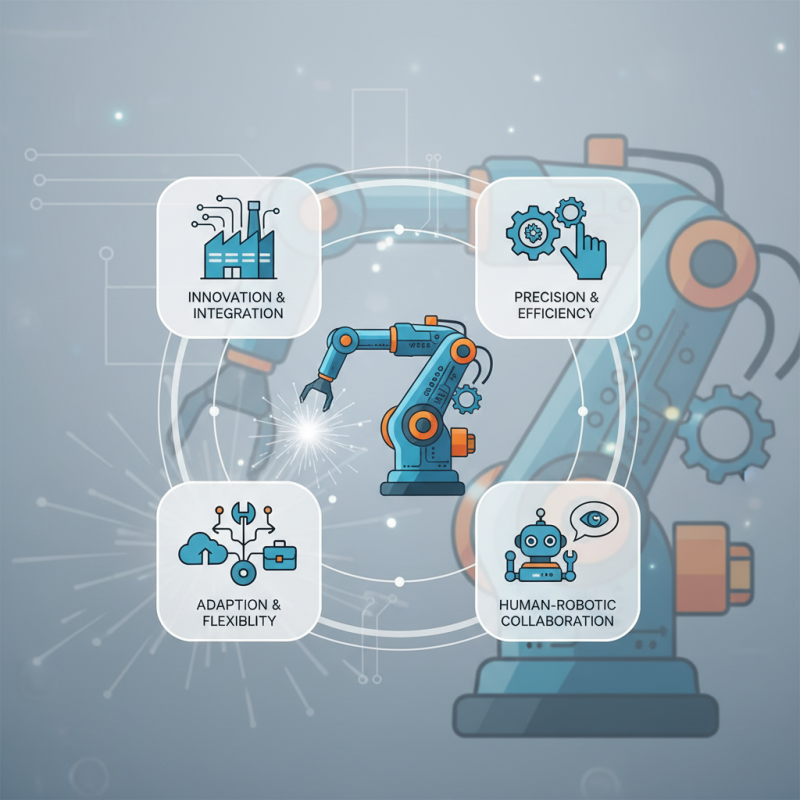
The landscape of robotic welding automation is rapidly evolving. In 2026, several key developments are set to influence this field. One significant trend is the integration of artificial intelligence. AI can enhance decision-making and improve weld quality. It allows robots to adapt to different materials and configurations with ease. Such flexibility will likely transform production lines.
Another important advancement is the development of advanced sensors. These sensors enable real-time feedback during the welding process. The ability to monitor and adjust parameters on the fly can lead to higher efficiency and reduced defects. Moreover, the use of machine learning in welding offers the potential to predict issues before they occur.
Tip: Regular training for operators is essential. Even with advanced technology, human oversight remains vital. Operators should understand both the machine and the welding process.
Moreover, as automation increases, companies must reassess their workforce needs. Robots do not eliminate the need for skilled workers but change their roles. There will be a greater focus on data analysis and system maintenance.
Tip: Investing in employee training programs can bridge the skill gap. By upskilling the workforce, companies can prepare for future changes effectively.
In summary, robotic welding automation is on the brink of major advancements. AI, advanced sensors, and workforce adaptation are pivotal. The journey ahead requires both technological innovation and human oversight.
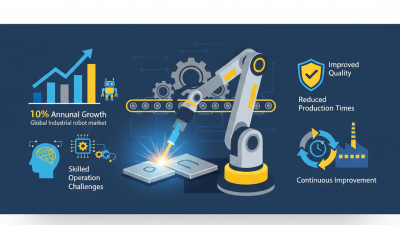
Robotic welding is rapidly transforming various industries.
According to a recent report, the global market for robotic welding is expected to reach $4.79 billion by 2026.
This surge reflects the rising need for automation in manufacturing processes. Industries like automotive and aerospace are leading the way.
They rely heavily on robotic welding for precision and efficiency.
In manufacturing, robots handle repetitive tasks with unmatched speed.
This reduces human error and improves safety conditions.
For instance, a study showed that robotic systems can increase productivity by up to 25%.
However, integrating such advanced technology is not without challenges.
Some companies struggle with initial costs and workforce adaptation.
Employee training is essential for maximizing the benefits of automation.
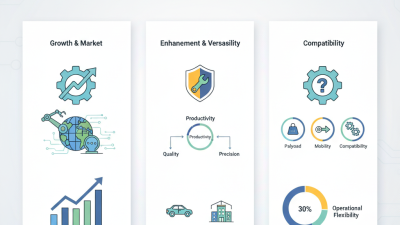
Emerging applications extend beyond traditional sectors.
Robotics are now used in construction and healthcare as well.
In construction, they are employed for tasks like steel fabrication.
In healthcare, they assist in the production of medical devices.
Yet, adoption rates vary widely. Companies must address compatibility issues with existing systems.
Future trends will likely focus on enhancing flexibility and collaboration between humans and machines.
The impact of AI and machine learning on robotic welding automation is transforming the industry. These technologies enhance precision and efficiency. Machines can now learn from past welds, improving their performance over time. This ability reduces defect rates and boosts productivity.
Tips: Consider integrating machine learning algorithms to analyze welding data. This can help identify patterns and improve decision-making. Implementing small changes can lead to significant improvements.
Despite advances, challenges remain. Not all welding jobs are suited for automation. Complex tasks often require human oversight. However, robots can assist with repetitive tasks, freeing workers for more intricate work.
Tips: Regularly assess the tasks your robots perform. Are they addressing the most challenging aspects? Feedback from workers can provide insights for better implementation. Integrating human expertise with machine learning can create a more effective welding process.
| Trend | Description | Impact Level (1-5) | Adoption Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI Integration | Incorporation of AI to enhance decision-making and adaptability in welding processes. | 5 | 60 |
| Machine Learning Optimization | Use of machine learning algorithms to optimize welding parameters in real-time. | 4 | 50 |
| Remote Monitoring | Enhanced capability for operators to monitor and control operations remotely. | 4 | 55 |
| Collaboration with Cobots | Increased utilization of collaborative robots (cobots) alongside humans for safety and efficiency. | 5 | 65 |
| Predictive Maintenance | Implementation of predictive maintenance strategies to minimize downtime. | 3 | 45 |
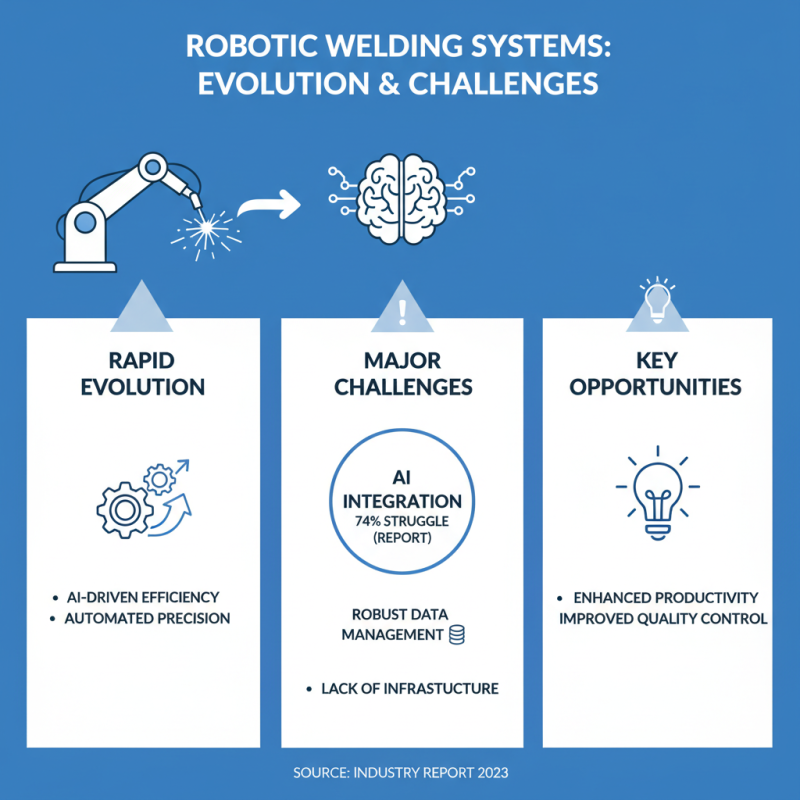
The landscape of robotic welding systems is evolving rapidly. However, several challenges stand out. One major concern is the integration of advanced artificial intelligence. A recent report revealed that 74% of companies struggle with AI implementation in welding processes. AI promises efficiency, but it also requires robust data management. Many organizations lack the infrastructure to support this shift.
Training employees is another critical issue. Skilled technicians are essential for overseeing robotic systems. Yet, only 30% of workers currently possess the necessary skills. Companies face the risk of productivity loss as they transition to automated processes. If they do not invest in upskilling their workforce, they may fall behind.
Moreover, safety remains a top priority. Automation can reduce human error, but it also creates new hazards. Recent statistics indicated that 43% of industrial accidents still involve automated equipment. Regular assessments and updates to safety protocols are necessary to address emerging risks. Balancing the benefits of automation with safety concerns continues to be a significant challenge for the industry.
Sustainability in robotic welding is gaining traction. Recent reports indicate that automated systems can reduce waste significantly. For example, optimized welding processes can cut material usage by up to 30%. This is essential as manufacturers face increasing pressure to adopt greener practices.
Moreover, energy efficiency remains a concern. A study revealed that robotic systems can lower energy consumption by 20-40% compared to traditional methods. However, the initial setup costs can be high. Companies must weigh the long-term benefits against upfront investments.
Challenges also arise with technology maintenance. While automation promotes efficiency, downtime can hinder productivity. Regular maintenance is crucial to prevent costly interruptions. Balancing sustainability goals with operational efficiency is vital for manufacturers moving forward.