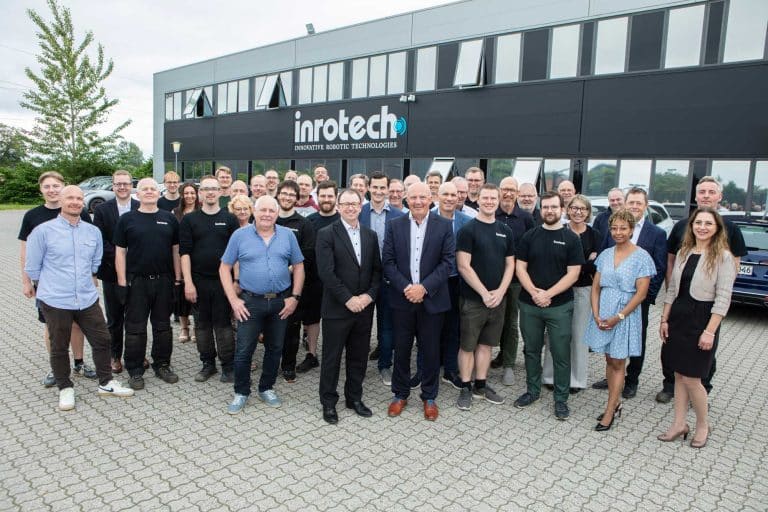
Lincoln Electric ® acquires Inrotech A/S
Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,

Vision-Based Adaptive Intelligence Software Extends Lincoln Electric’s Technology Platform -Lincoln Electric® is pleased to announce that it has acquired Inrotech A/S. Headquartered in Odense, Denmark,
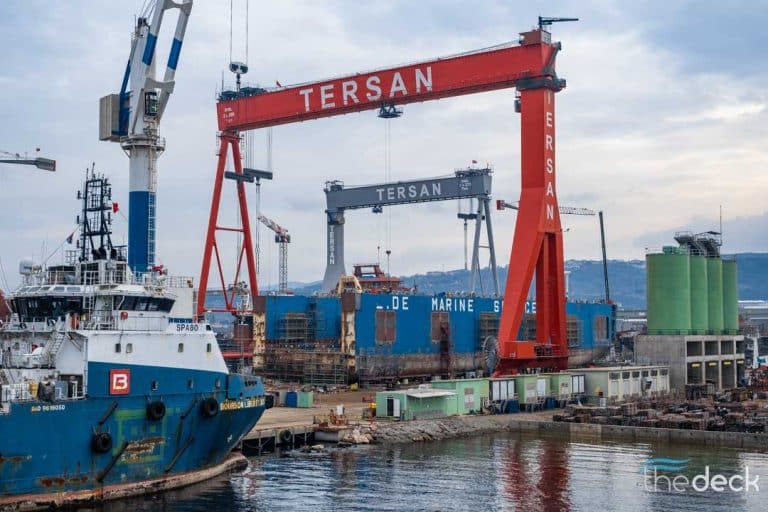

Inrotech has received an order from Tersan Shipyard, a diversified company with expertise in constructing LNG and battery-operated vessels, as well as various value-added niche

Inrotech welcomes Henrik Lenskjold as its new Chief Executive Officer. Henrik, who served as the Chief Operation Officer at Inrotech for six years, has been
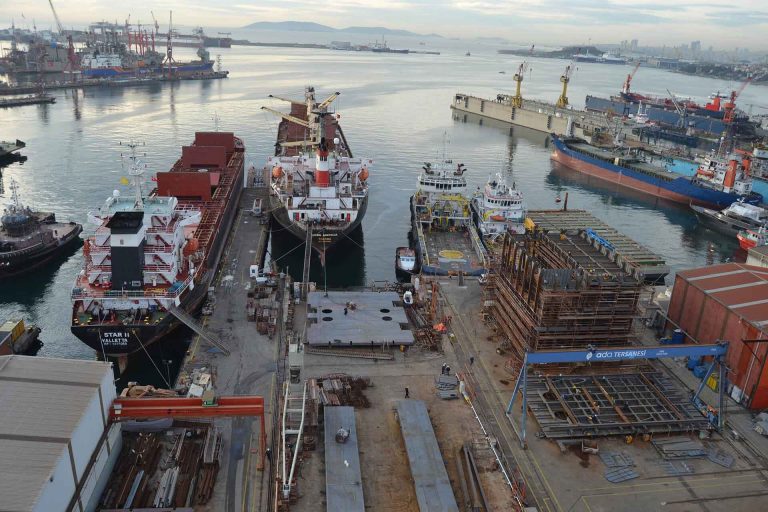

Welding robots originating from Denmark have gained substantial popularity within the Turkish shipbuilding industry for the welding of ship panels. Ada Shipyard, a prominent shipyard
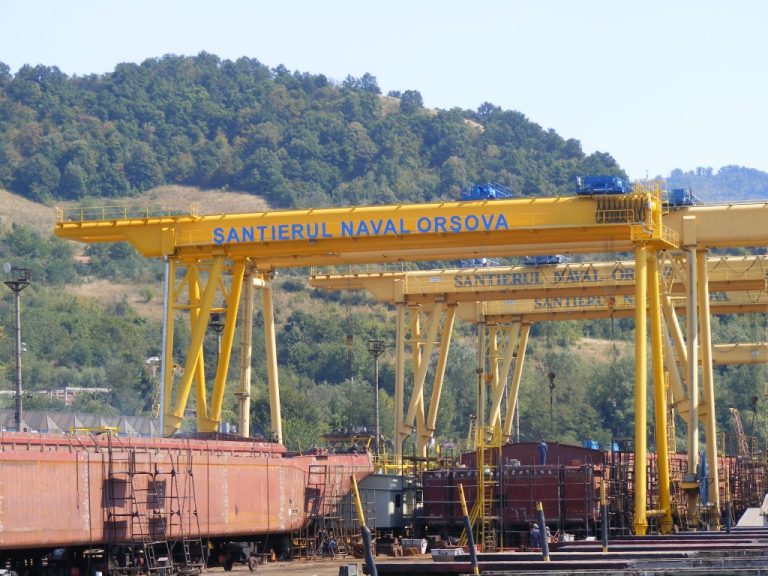

Inrotech has received an order from Santierul Naval Orsova Shipyard, a leading shipbuilder in Romania. The company invest in high quality welding automation as a

The growing need for skilled welders in offshore wind and shipyards worldwide has placed a huge demand for labor in these sectors. Numerous manufacturers experience
Automated welding systems are revolutionizing the manufacturing industry. These systems use advanced technology to perform welding tasks efficiently and accurately. They have a significant impact on productivity and quality control.
In many environments, automated welding systems can be more reliable than human welders. They can work continuously without fatigue, making them ideal for high-volume production. However, the initial setup and maintenance can be complex, requiring skilled technicians.
While these systems offer many advantages, there are challenges too. For instance, adaptability to new designs can be a concern. Changes in production demands may lead to underutilization. Companies must weigh the benefits against potential limitations to decide on implementation.

Automated welding systems are advanced technologies designed for welding applications. These systems utilize robots or automated machinery to perform welding tasks with high precision. The key component is a welding machine that can be programmed to work on various materials and shapes. This flexibility allows for efficient production across different industries.
These systems operate on pre-defined parameters. They can adjust welding speed and temperature based on the materials involved. The robots often work with sensors to gauge the quality of the weld. This real-time feedback helps in achieving consistent results. However, one must be cautious. Calibration errors can lead to defects, making regular maintenance essential.
Using automated welding systems can improve productivity significantly. They reduce human error and increase the speed of the welding process. Yet, there are challenges. The initial setup can be costly and complex. Operators need training to handle these advanced systems. This can sometimes lead to a steep learning curve. Overall, while these systems offer many advantages, their implementation requires careful planning and consideration.
Automated welding systems consist of several key components that work together to enhance precision and efficiency in welding operations. A typical setup includes a welding power supply, a robotic arm, and a control system. According to industry reports, the demand for automated welding has surged, with a market growth rate projected at over 6% annually. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on technology to improve production capabilities.
Robotic arms are crucial in these systems. They are programmed to execute precise movements, ensuring consistent weld quality. These arms can perform complex tasks, reducing human error and operational downtime. Many industries have reported a 50% increase in production speed when switching to automated systems. However, integrating these robots may require significant upfront investment and proper training for personnel, which can be challenging for some manufacturers.
The control systems manage all aspects of the welding process, from monitoring power levels to adjusting the speed of the robotic arm. Advanced software enables real-time data analysis, allowing for immediate adjustments to maintain optimal performance. While the benefits are clear, organizations must remain vigilant. A failure in the software can lead to defective welds, requiring additional checks and potentially delaying production. Balancing automation with oversight is an ongoing challenge in striving for perfection in automated welding.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Welding Robot | A programmable machine used to perform welding tasks. | Automates welding processes for higher precision and repeatability. |
| Control System | The software and hardware that manage the welding robot's actions. | Coordinates movements and adjusts parameters for optimal welding. |
| Welding Power Supply | Supplies the required electric current for the welding process. | Provides the necessary energy to melt and fuse the materials together. |
| Welding Torch | The tool used to direct the heat to the workpiece. | Focuses heat and filler material to join metals effectively. |
| Feed Mechanism | Feeds filler material into the welding area as needed. | Ensures a continuous supply of filler material for better weld quality. |
| Safety Equipment | Includes gear like helmets and barriers to protect workers. | Ensures safety during operation to prevent accidents. |
Automated welding techniques are essential in various industries. They increase efficiency and ensure high-quality welds. Popular methods include MIG, TIG, and laser welding. Each technique has unique applications and benefits.
MIG welding, or Gas Metal Arc Welding, uses a continuous wire feed. It creates a strong bond quickly. This technique is often used in automotive manufacturing. However, it may produce more spatter than other methods. This downside can lead to additional cleanup.
TIG welding, or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, is known for precision. It uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode. This makes it ideal for thin materials and complex shapes. However, it requires skilled operators and can be time-consuming. Finally, laser welding offers speed and accuracy. It focuses a high-powered laser beam on the materials. While effective, initial setup costs can be high. Each technique has its strengths and weaknesses. Understanding them helps in choosing the right process for specific tasks.
This chart illustrates the popularity of various automated welding techniques. MIG welding remains the most widely used method, accounting for 45% of the market, followed by TIG and stick welding with 25% and 15% respectively. Submerged arc and plasma arc techniques have a smaller share at 10% and 5%.
Automated welding systems have revolutionized manufacturing processes. These systems operate using programmable robots that complete welding tasks with high precision. Typically, a welder sets the parameters for the materials and type of welding needed. The machine then executes these instructions, often with minimal human intervention. In fact, industry reports show that automated welding can improve productivity by up to 50% compared to manual methods.
The operation of these systems relies on several components. Robotics, sensors, and software all play vital roles. Robots equipped with advanced sensors can detect and adjust to variations in the materials being welded. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining quality. Yet, improper calibration can lead to defects. Such mistakes can be costly and time-consuming.
Tips: Regular maintenance is essential. Schedule routine checks for all components. Verify that software updates are applied. Training operators to recognize malfunction signs can prevent breakdowns. Additionally, consider conducting audits on welding parameters periodically. This helps ensure compliance with manufacturing specifications.
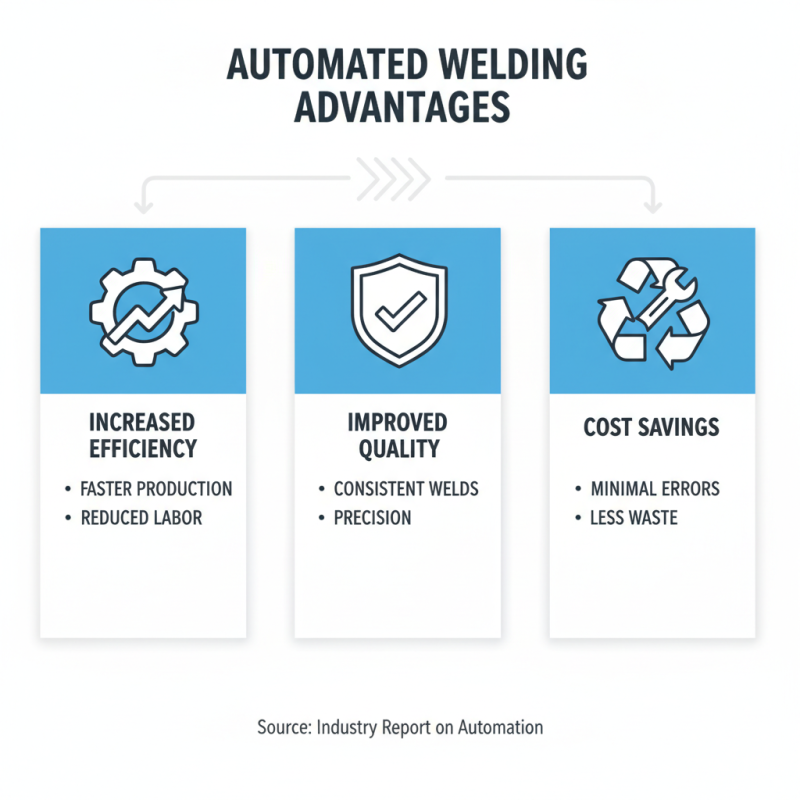
Automated welding systems offer significant advantages in various industries. They improve efficiency by reducing manual labor. This leads to faster production times. Additionally, consistency in weld quality is greatly enhanced. Automated systems can achieve precision beyond human capability. They operate with minimal errors, lowering material waste.
These systems find applications in automotive manufacturing, construction, and shipbuilding. In automotive plants, they create complex structures with ease. In construction, they join heavy metal beams accurately. However, the transition to automation is not seamless. Workers may need retraining for new technologies. The upfront cost of these systems can also be a hurdle. Nonetheless, many industries are embracing this innovation, recognizing its long-term benefits.